The F-16 Fighting Falcon, originally developed by General Dynamics (now part of Lockheed Martin), emerged from the U.S. Air Force’s Lightweight Fighter program in the early 1970s. This initiative aimed to produce an affordable but highly effective aircraft to support the larger F-15 Eagle. Its first flight took place in 1974—an unplanned lift-off during a high-speed taxi test that immediately highlighted the jet’s natural agility. When it officially entered service in 1978, the F-16 introduced several pilot-focused innovations, including a frameless bubble canopy for superior visibility, a side-mounted control stick for fine maneuvering, and a reclined seat to ease the effects of high-G forces. Its streamlined design—with cropped-delta wings and a smoothly blended wing and fuselage—made it well suited for both aerial combat and strike missions.
One of the F-16’s most groundbreaking elements is its adoption of a full fly-by-wire control system, making it the first fighter to rely completely on electronic rather than mechanical inputs. Coupled with its intentionally unstable “relaxed stability” configuration—continuously adjusted by onboard computers—this system enabled exceptional agility, allowing the jet to execute rapid rolls and tight turns. Powered by a single turbofan from either Pratt & Whitney or General Electric, the aircraft can surpass Mach 2 and field a wide array of weapons, from air-to-air missiles to precision-guided munitions. Its adaptability has made it a mainstay in roles ranging from dogfights to ground attack, reinforcing the “Fighting Falcon” moniker.
The F-16’s worldwide footprint is remarkable: more than 4,500 have been built and supplied to over 25 nations, making it one of the most widely produced and widely used fighter jets ever. It has participated in major operations such as Desert Storm—where it flew thousands of missions—and continues to support NATO and allied forces around the globe. Cost-effective yet highly capable, the F-16 became the preferred solution for many air forces seeking strong performance without excessive expense. Through upgrade efforts like the Mid-Life Update, which enhanced its sensors and weapon systems, the aircraft has remained relevant. Modern versions such as the Block 70/72 ensure that the F-16 continues to be a formidable platform decades after it first took to the sky.
Danish Air Force F-16 AM / BM
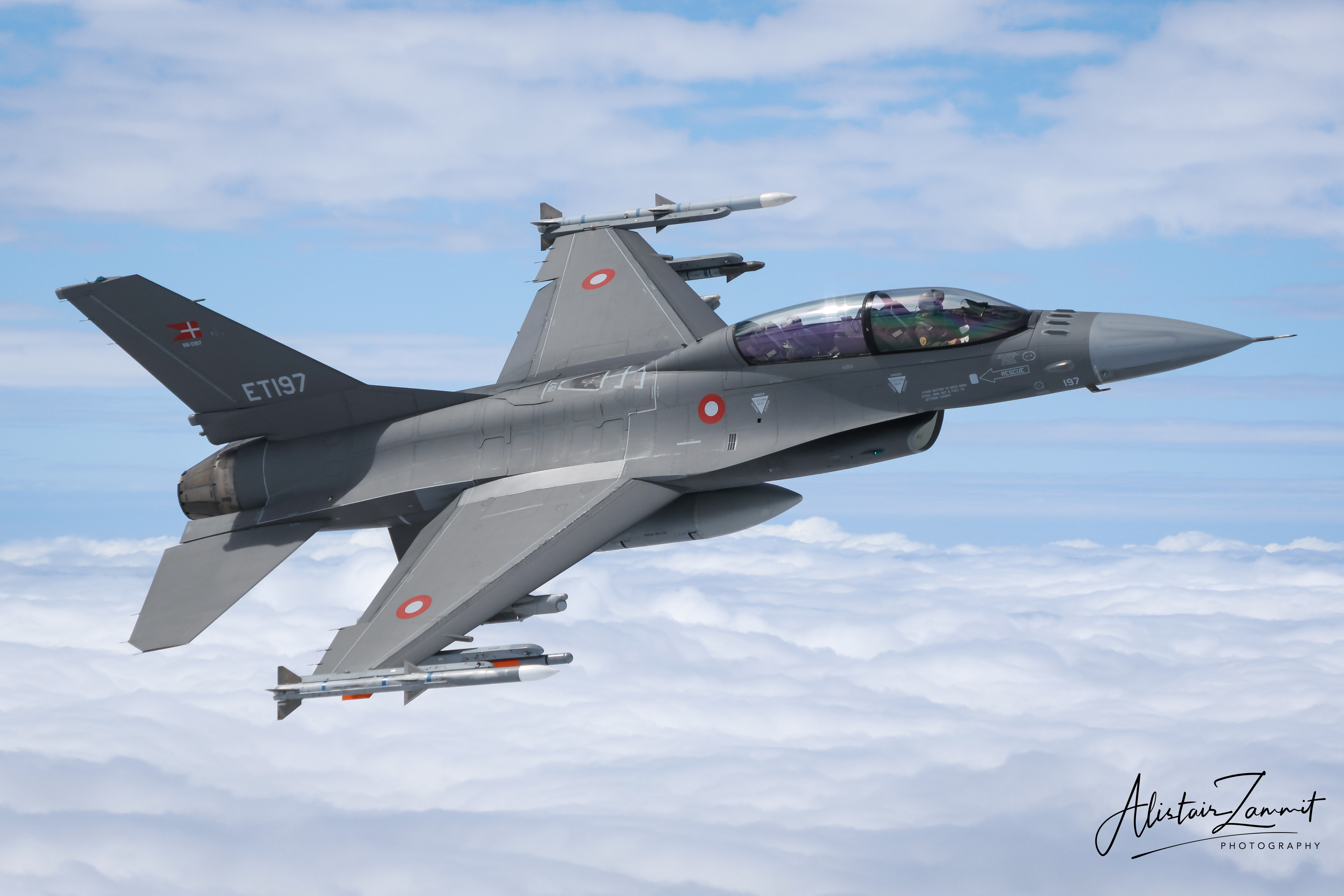
The Royal Danish Air Force (RDAF) adopted the F-16 Fighting Falcon in the late 1970s as part of a broader NATO initiative to harmonize fighter fleets across member nations. Denmark purchased 58 F-16A and 12 F-16B models, with deliveries beginning in 1980, replacing its aging F-100 Super Sabres and F-104 Starfighters. Initially stationed at Skrydstrup Air Base—and later also at Aalborg Air Base—the new jets significantly strengthened Denmark’s air defense and strike capabilities. Danish F-16s quickly became a regular presence in NATO training exercises and multinational missions, underscoring the country’s commitment to alliance operations.
During the 1990s, Denmark participated in the Mid-Life Update (MLU) program, modernizing its fleet with enhanced radar, avionics, and weapon systems to extend operational longevity. The RDAF’s F-16s saw combat in Operation Allied Force over Kosovo in 1999, flying both patrol and attack missions, and again during NATO’s campaign in Libya in 2011, when they carried out precision air-to-ground strikes. These missions emphasized the importance of the F-16 in Denmark’s international security contributions. The fleet remained highly reliable thanks to sustained upkeep and modernization.
By 2023, Denmark began transitioning to the F-35 Lightning II, following initial aircraft deliveries in 2021, gradually retiring its F-16s. Even during this shift, the F-16 continued to support NATO operations. Its long tenure in Danish service highlights the aircraft’s durability and reflects the strong defense relationship between Denmark and the United States within NATO, maintaining national airpower until the F-35 becomes fully operational.
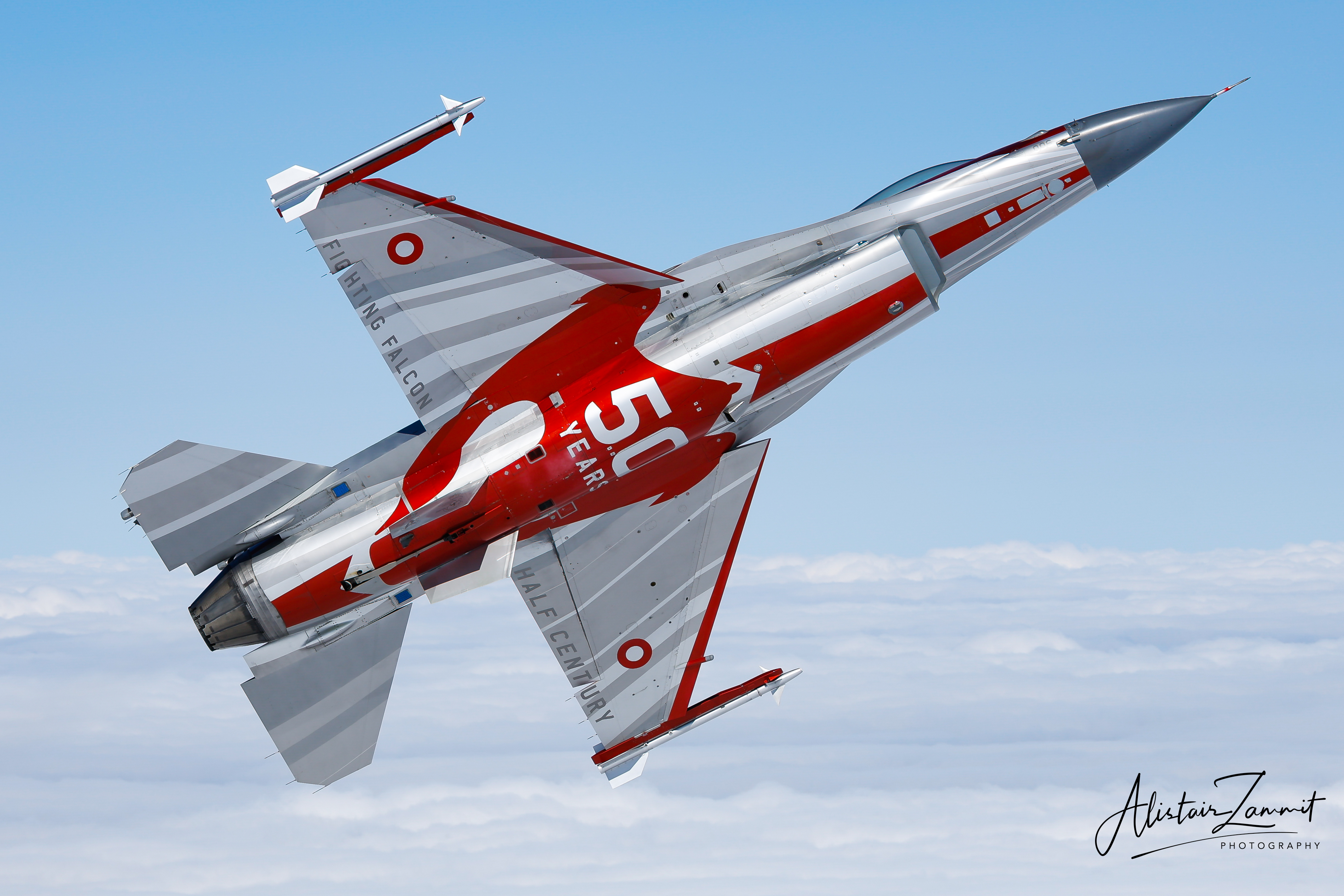
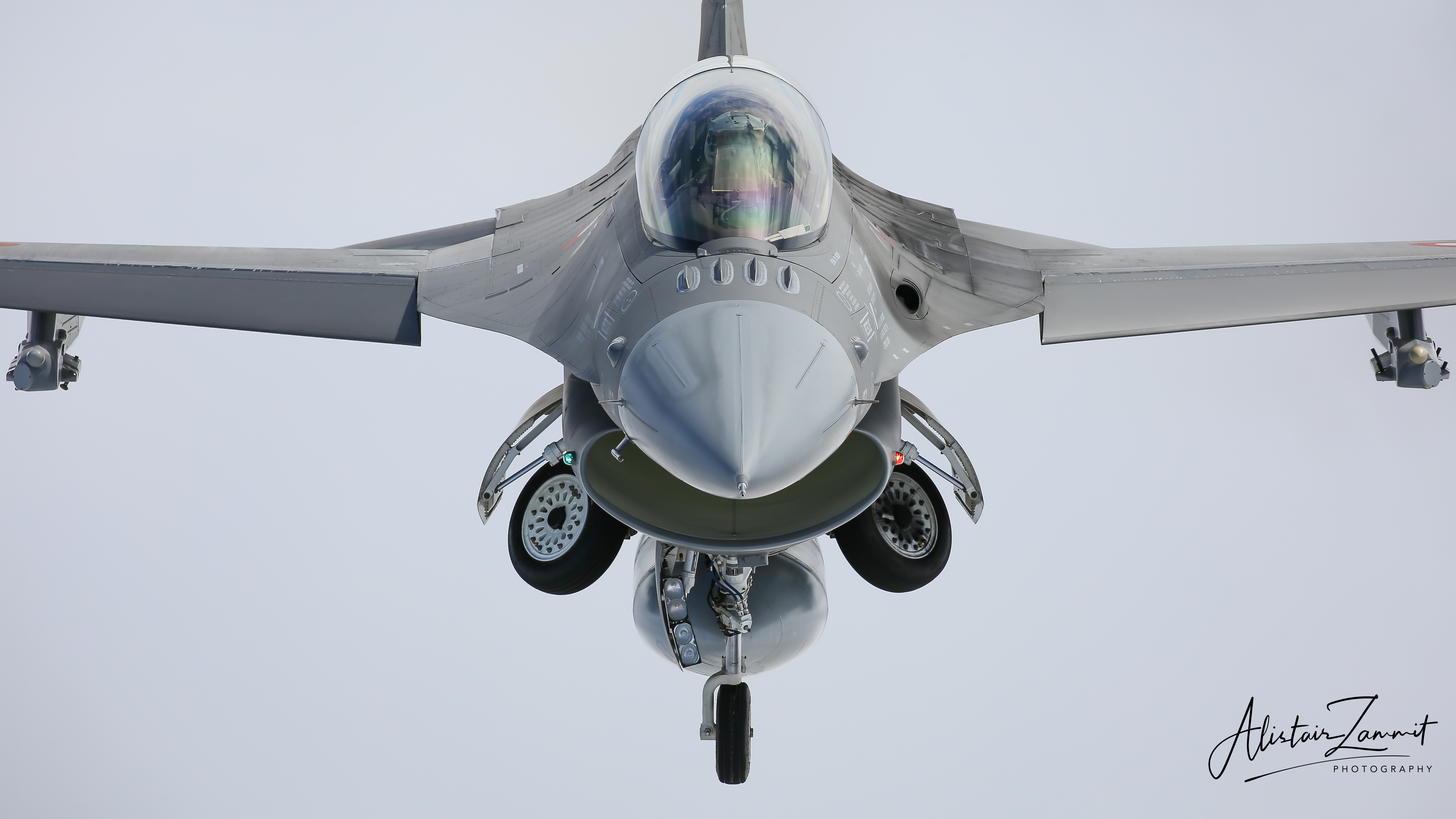
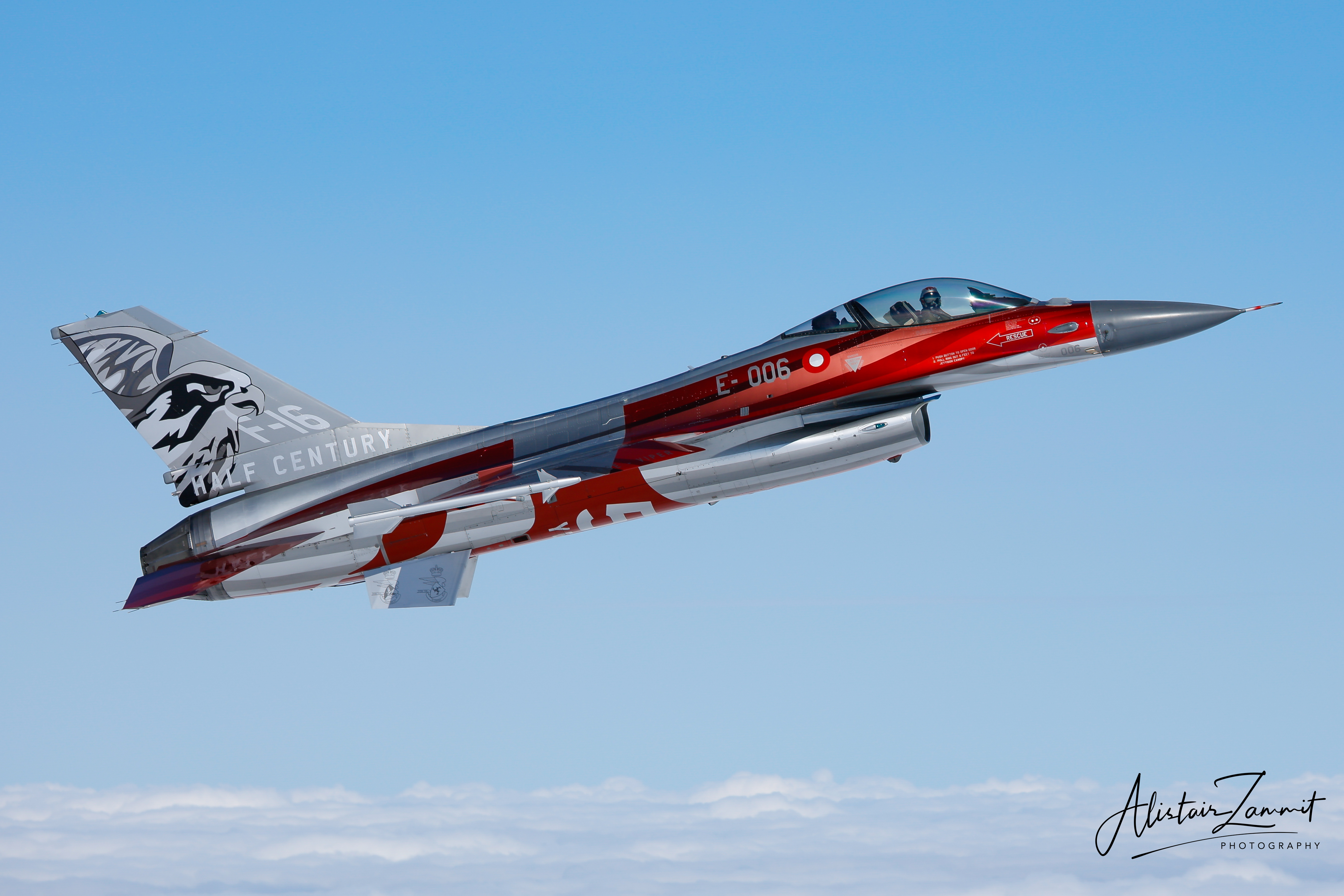













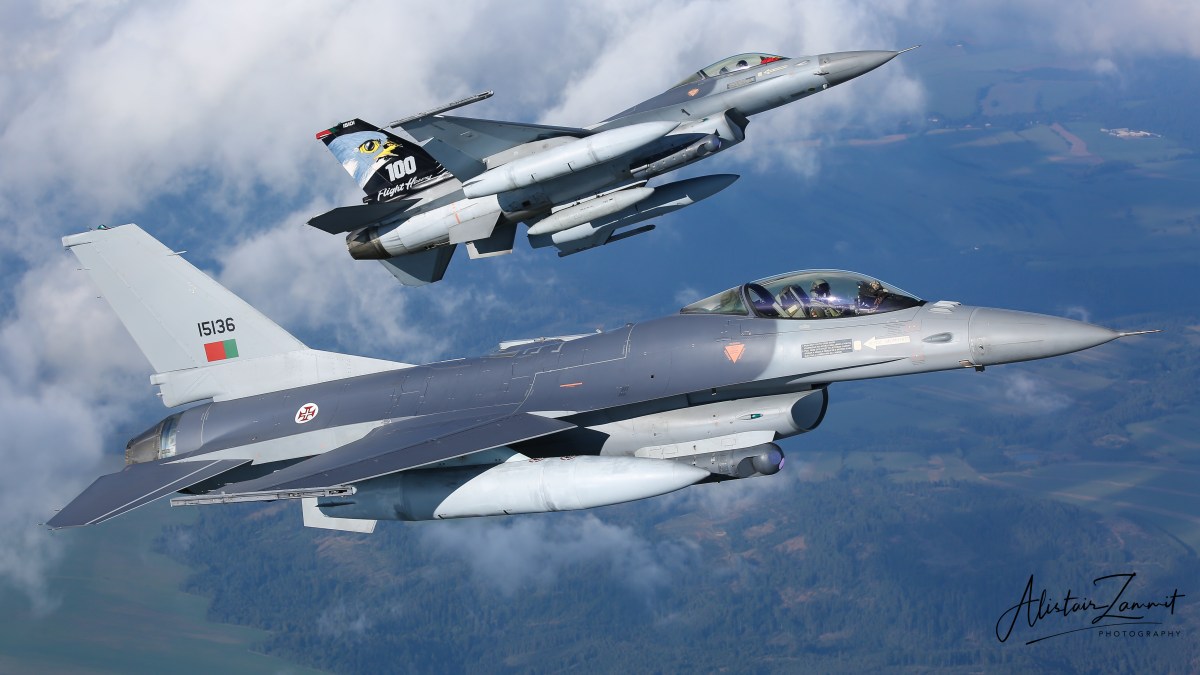
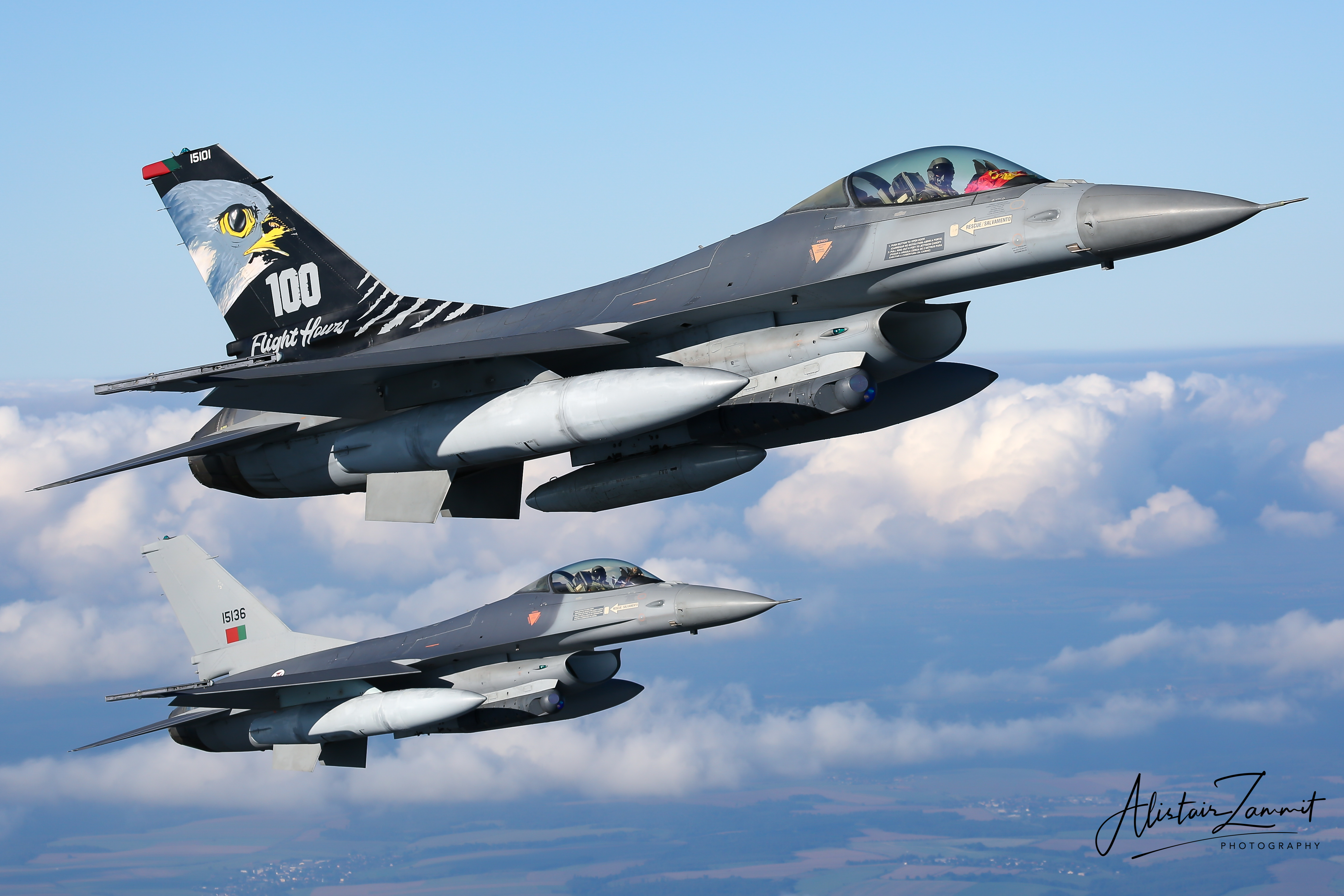
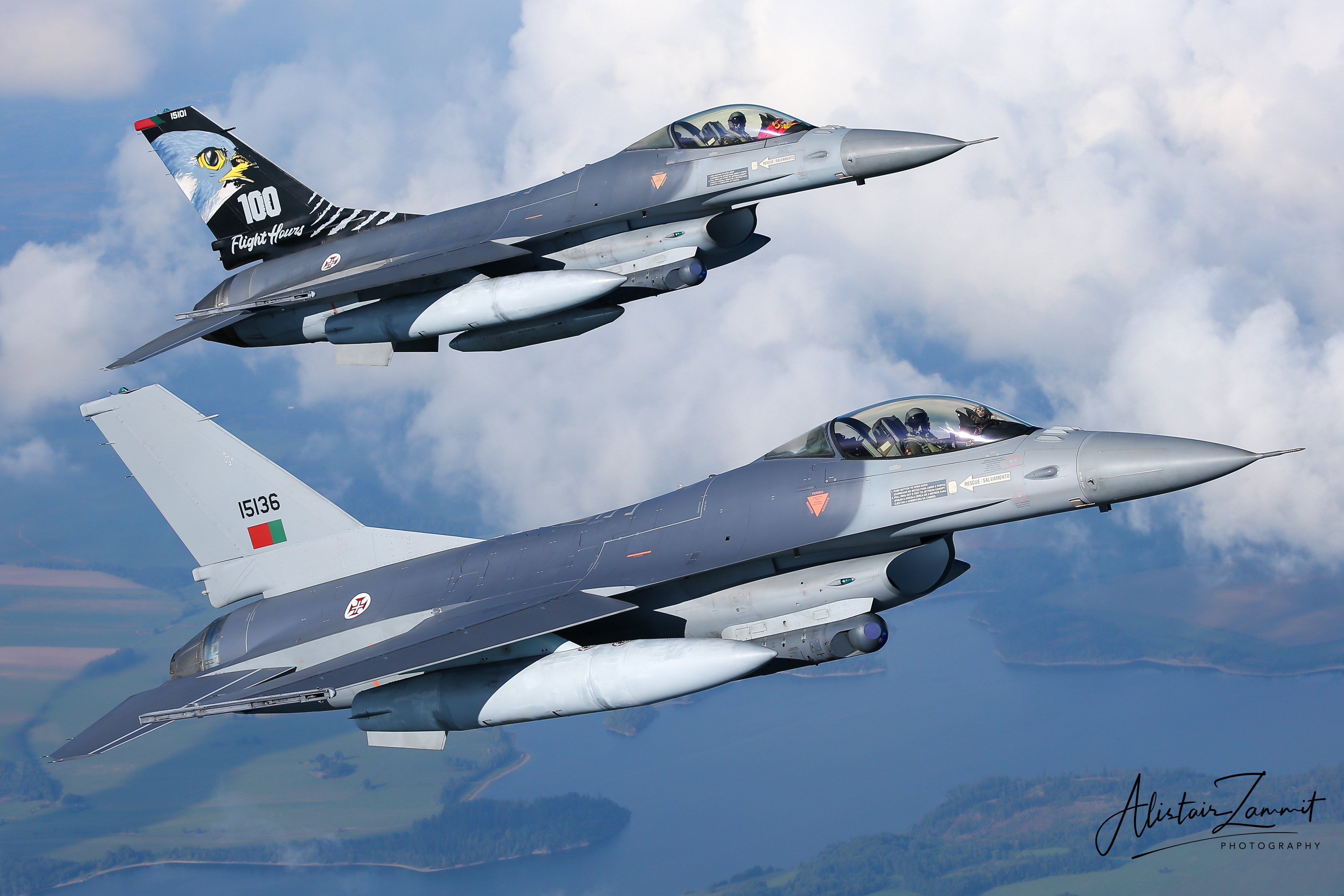
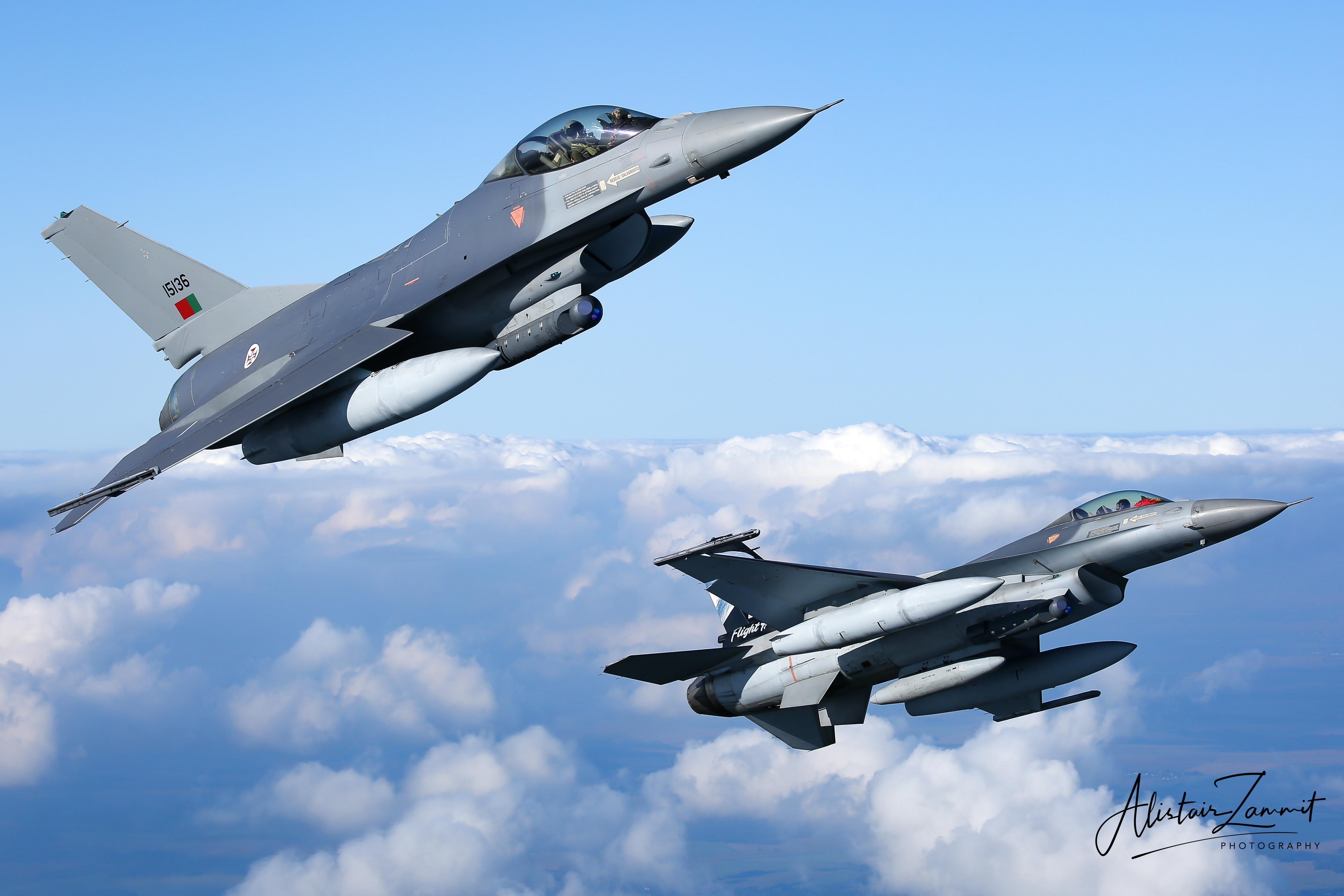
Portuguese Air Force F-16AM











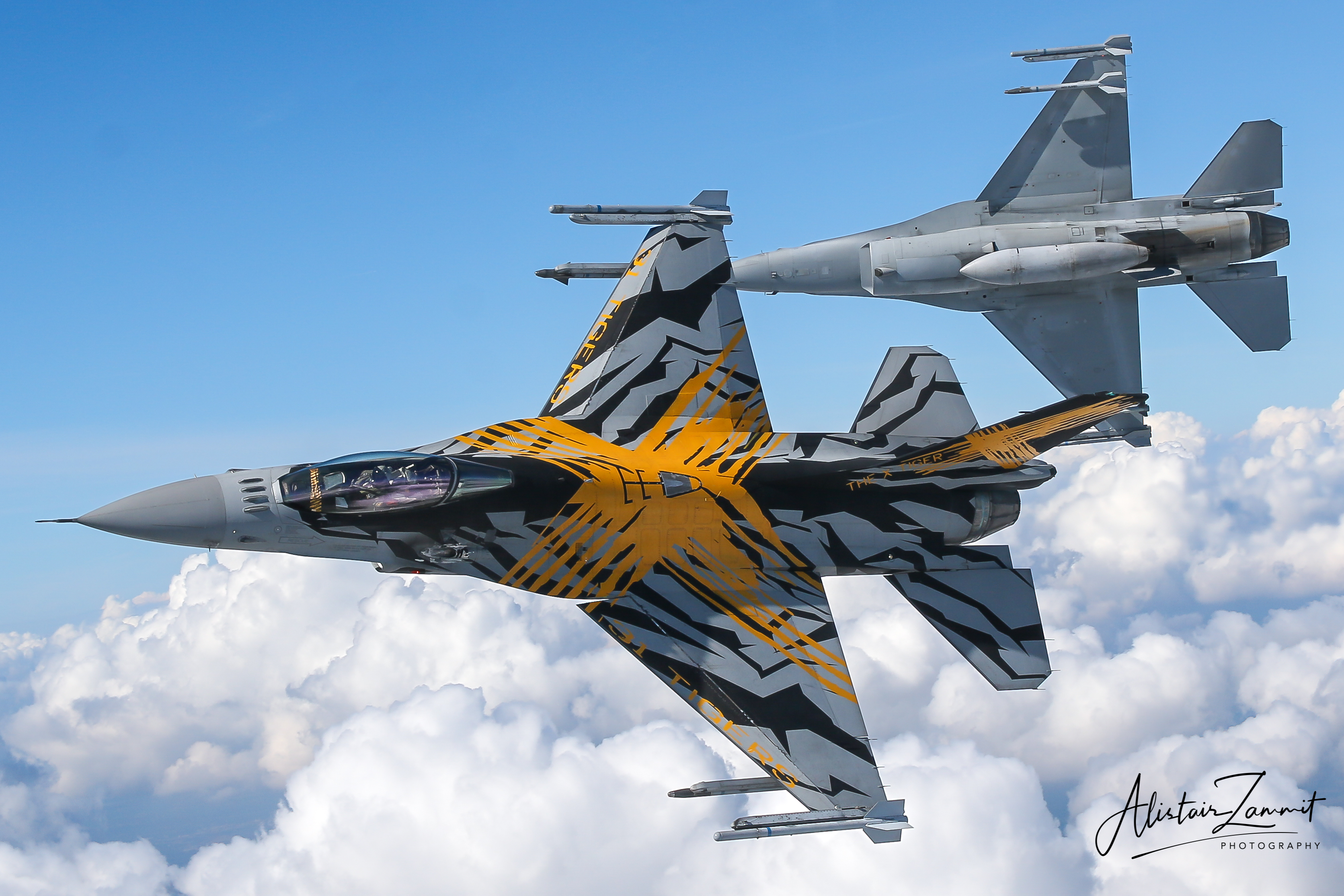
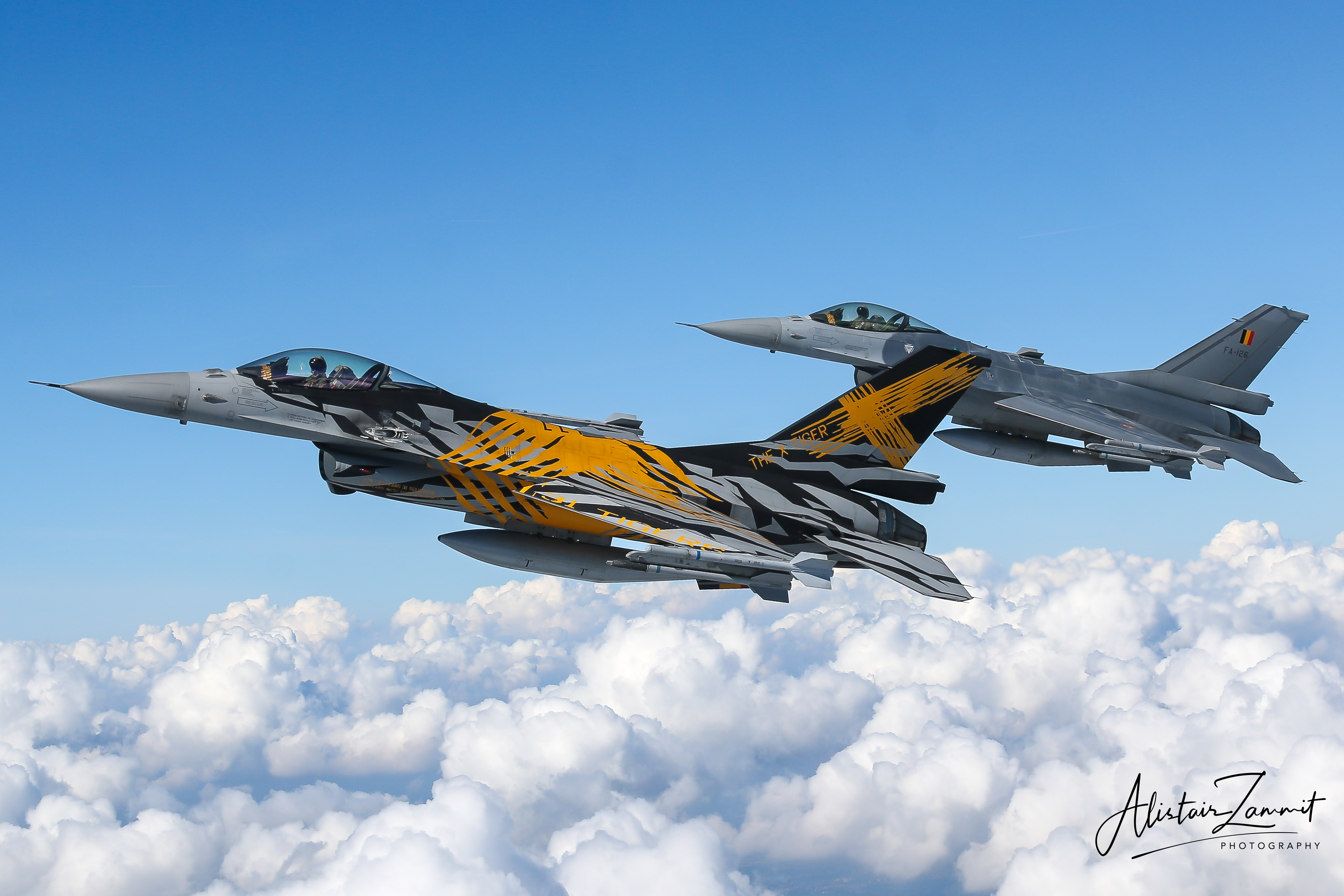
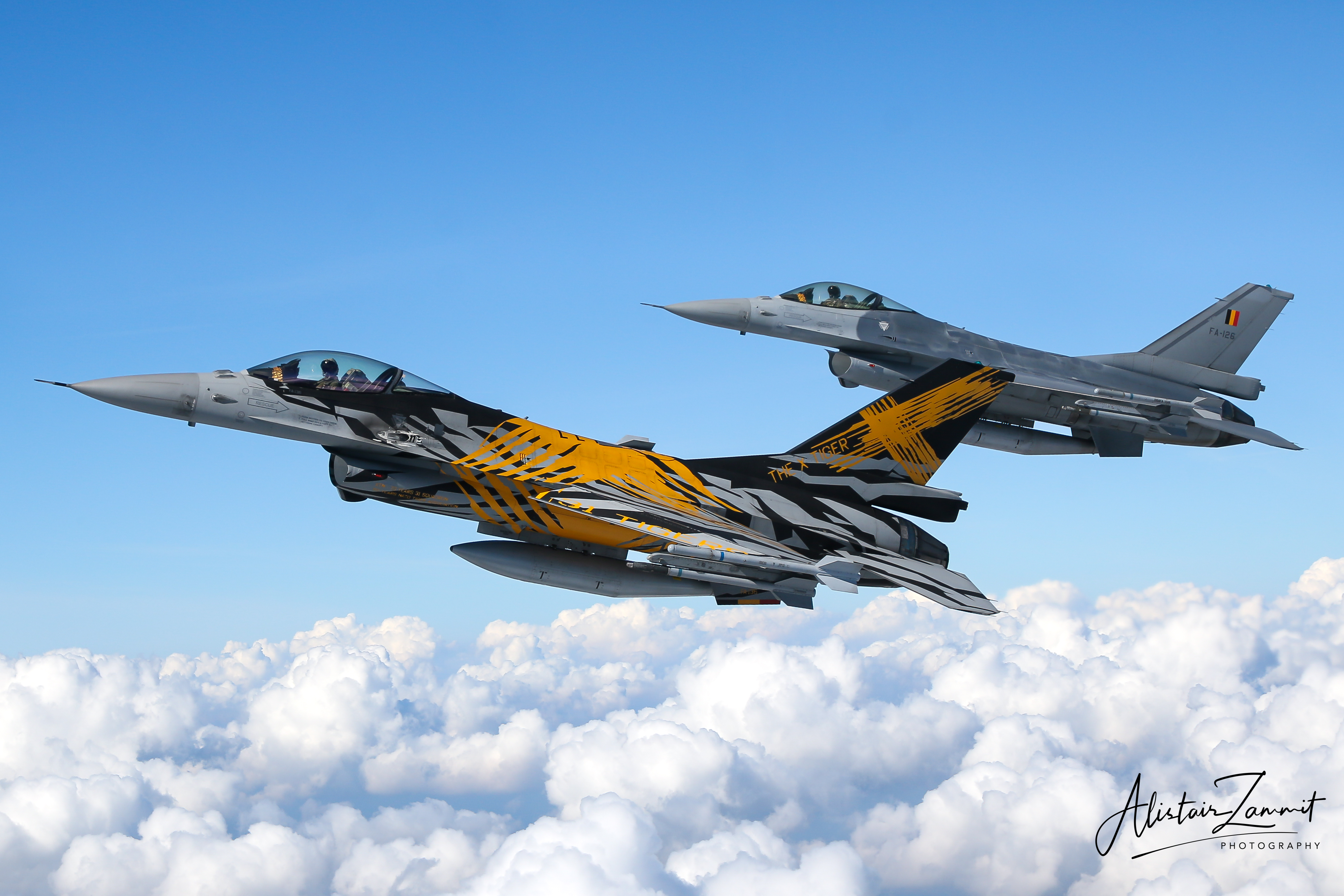
Belgian Air Force F-16AM








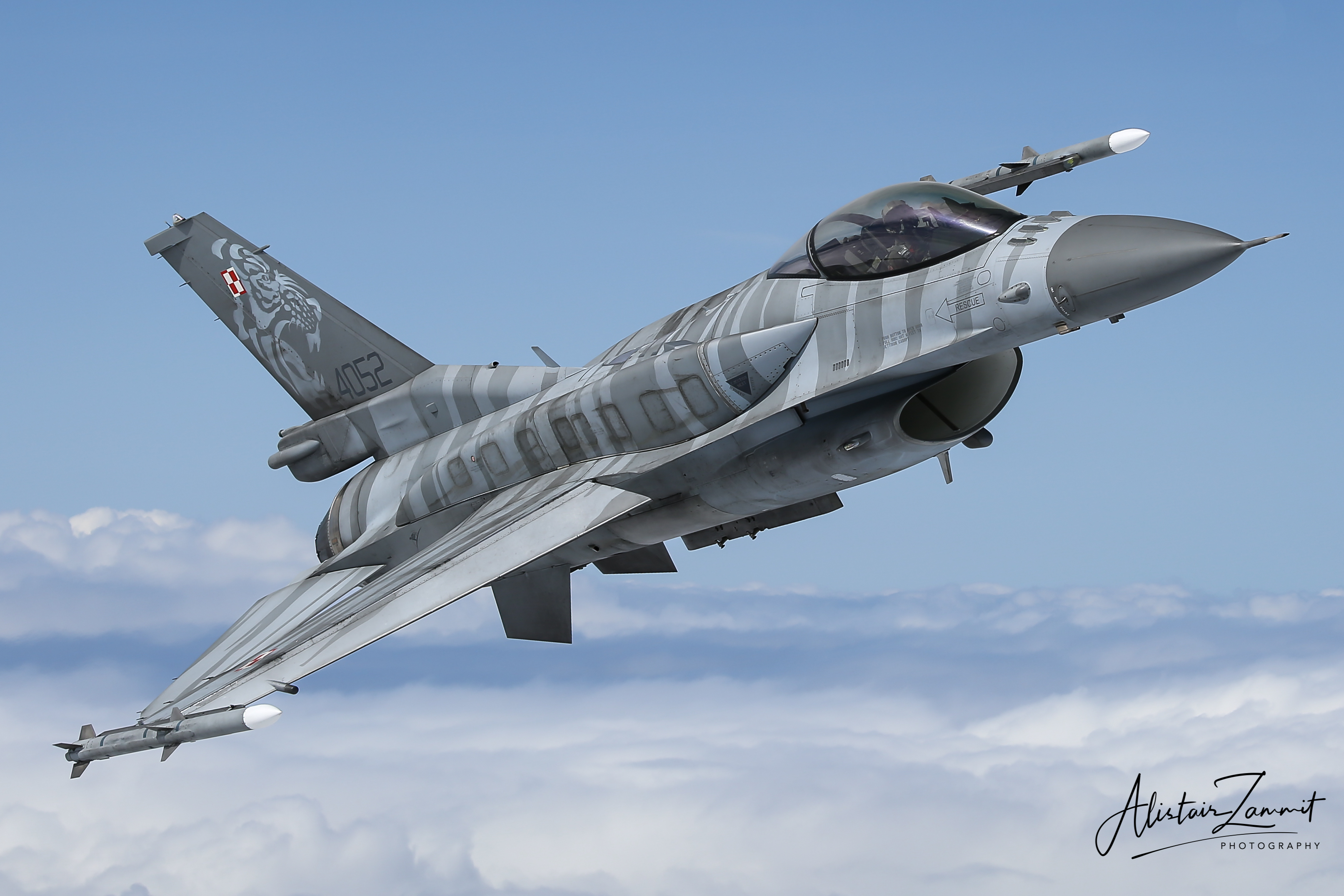
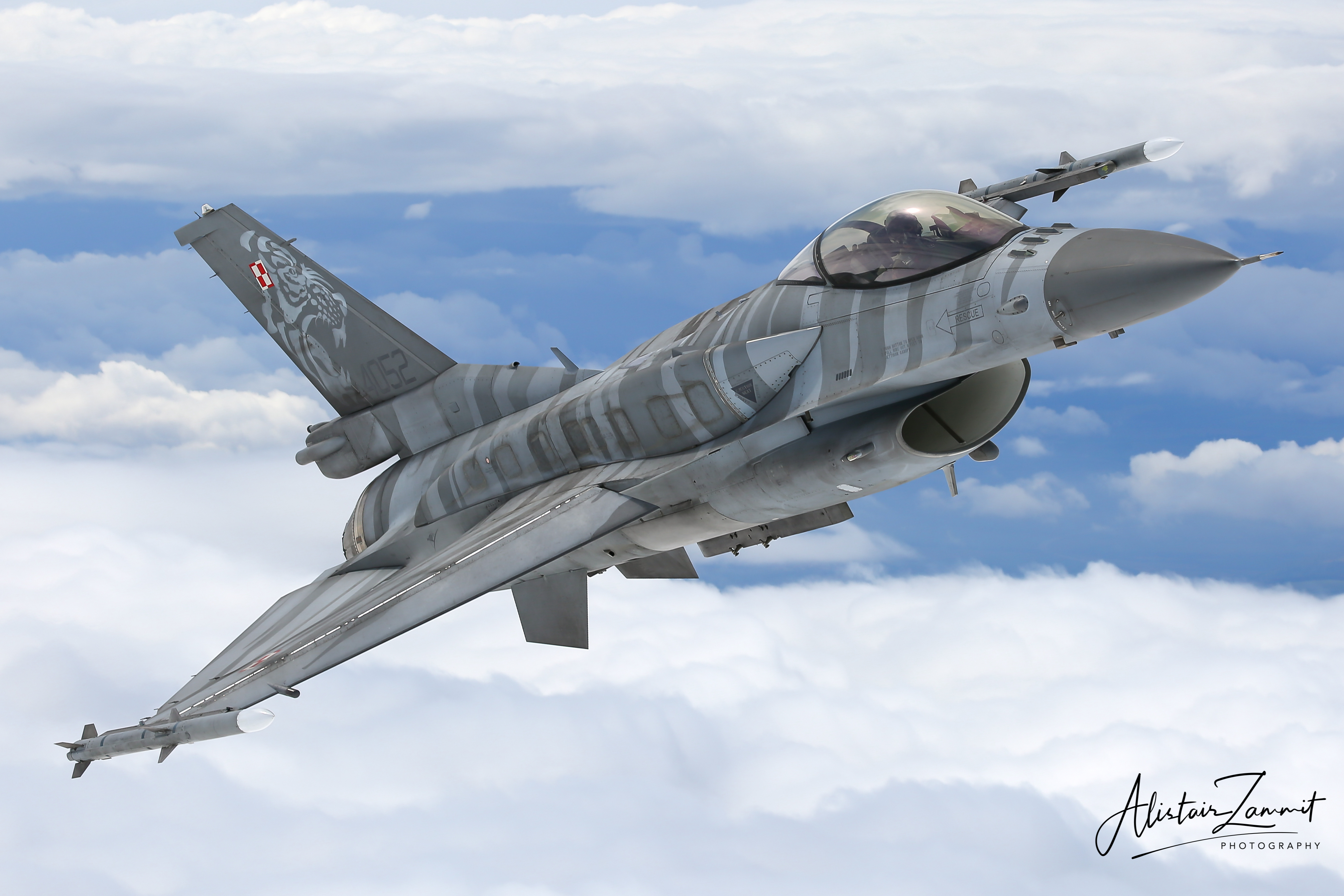
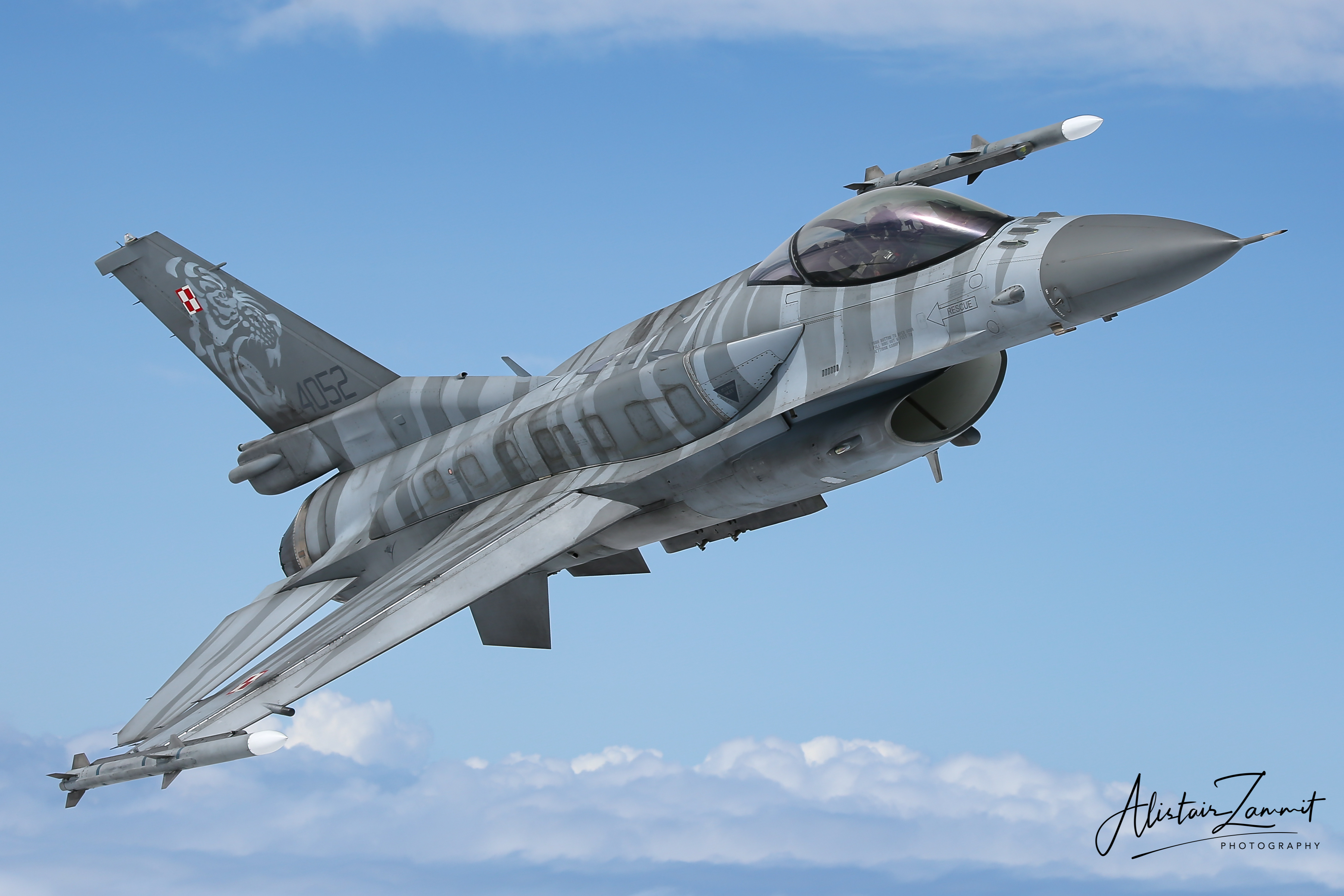
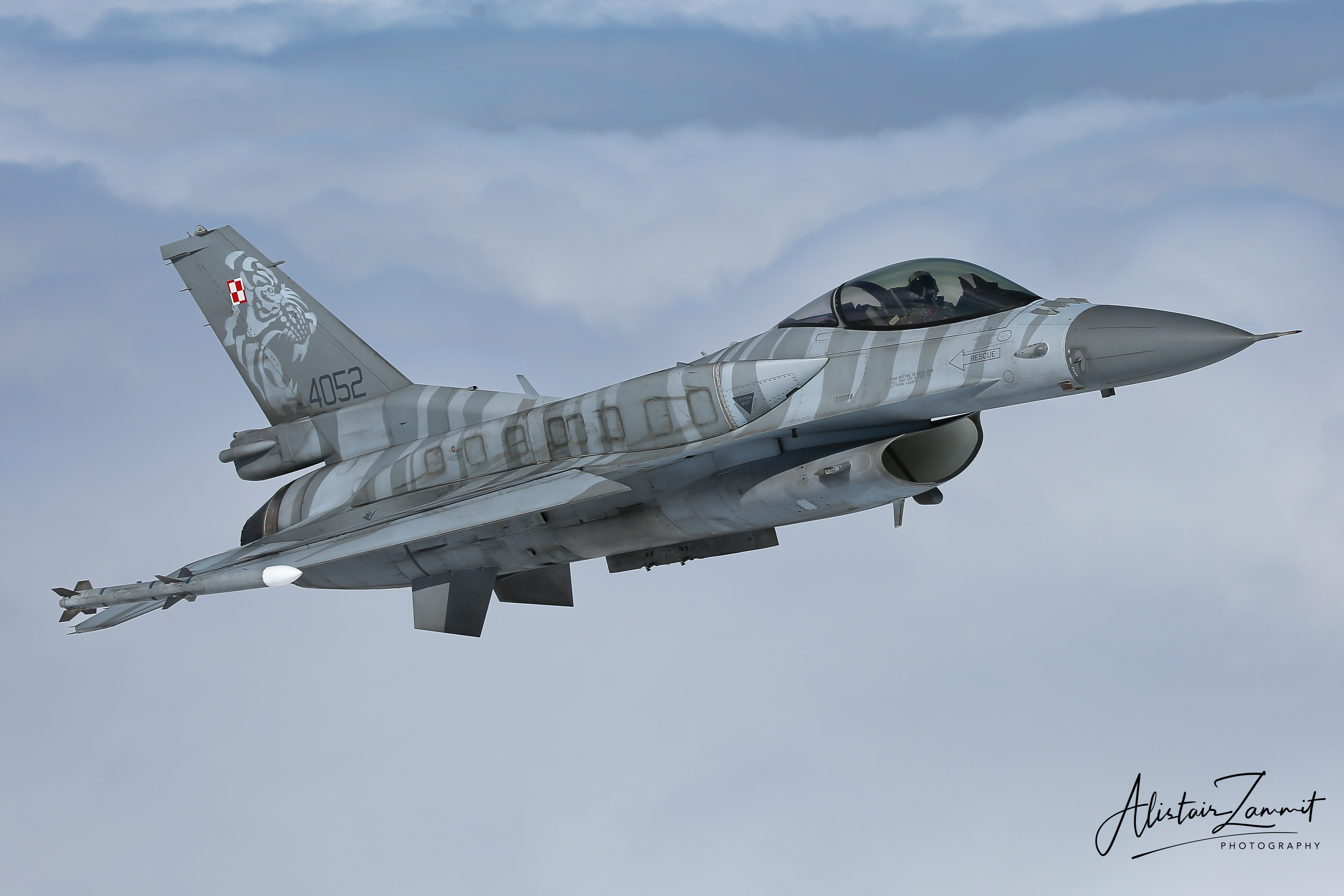
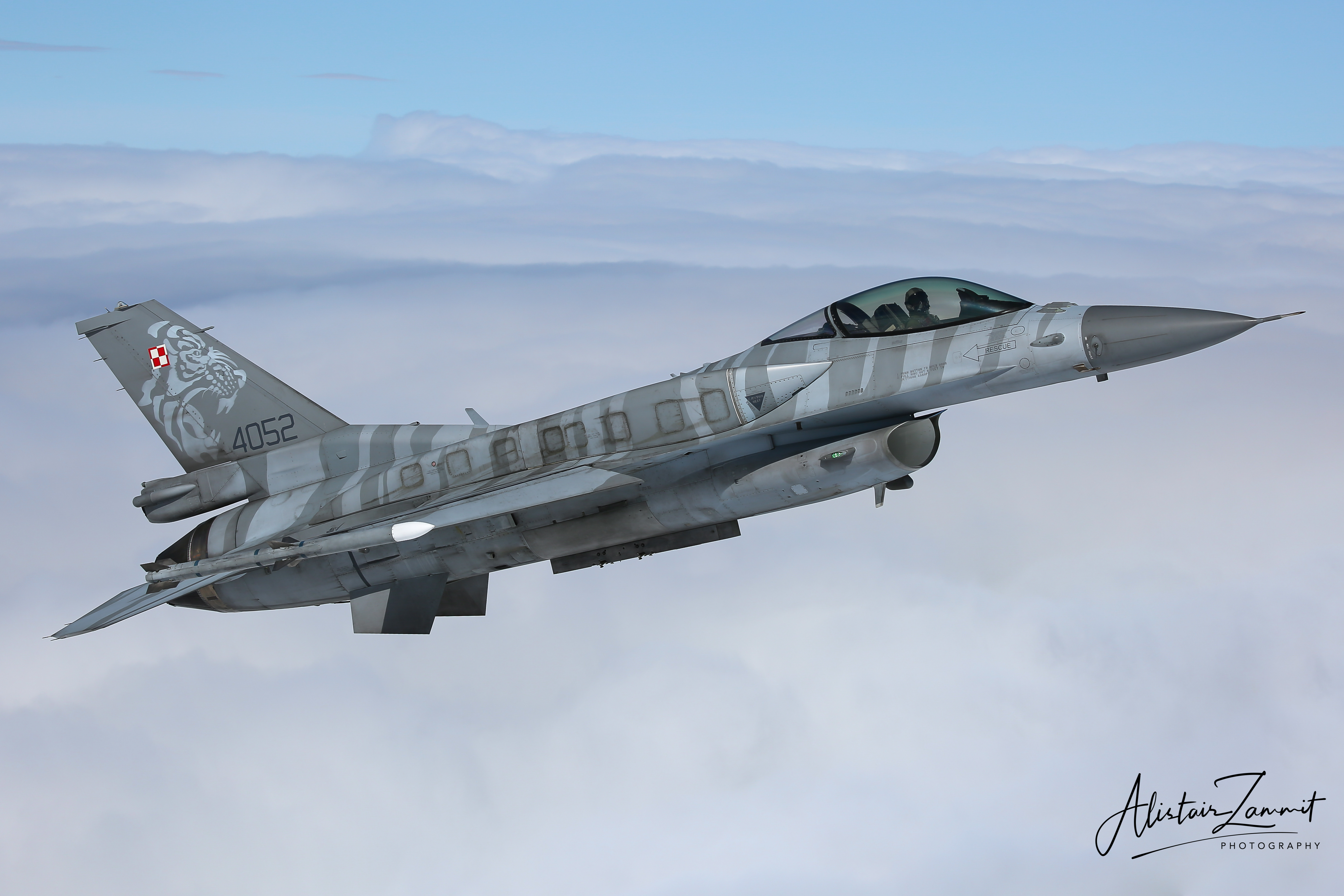
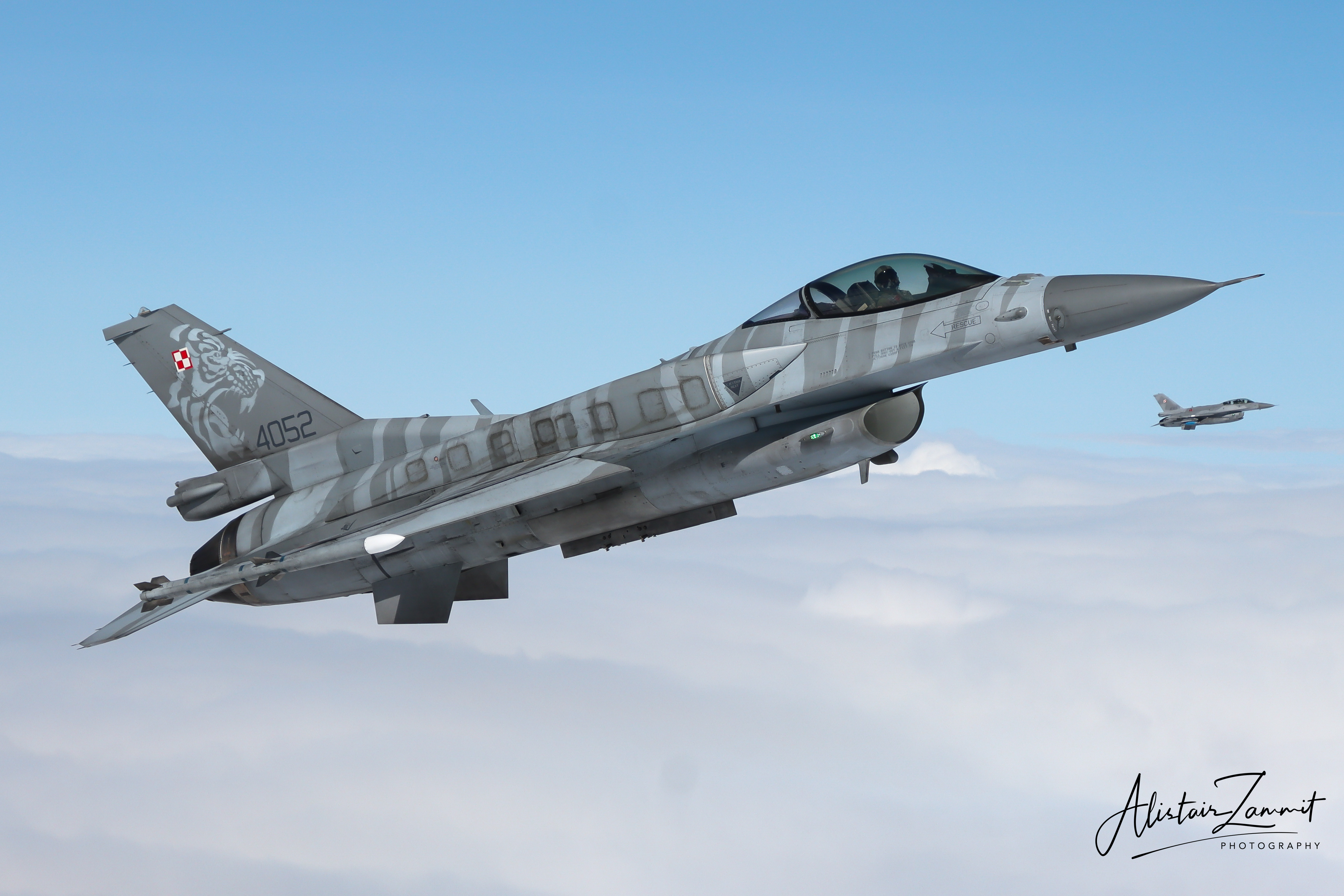
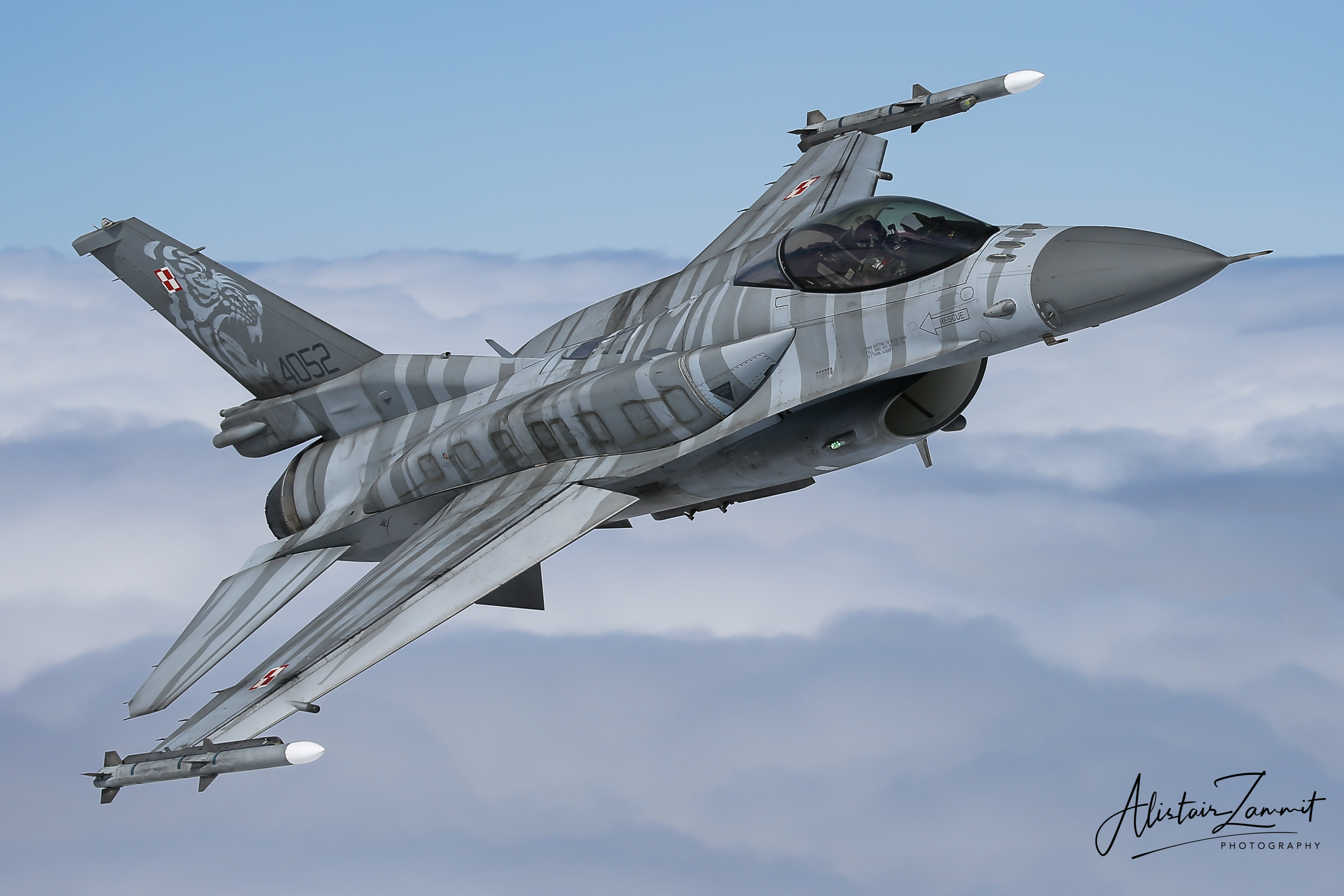
Polish Air Force F-16C